In countries like Nigeria and Haiti, electricity blackouts are routine.
Power outages sometimes last for more than a week in Haiti, where only about 25 percent of the Caribbean nation’s 10.9 million people are connected to the power grid.
And in Nigeria, a country more than 200 million people call home, power companies provide electricity to only 45 percent of households. Losing power about once a day in the West African nation is the norm.
But in the United States, 100% of households have access to electricity and the population’s dependence on power makes providers essential to daily well-being from life-and-death health to information access.
The P&G power outage, which lasted from Oct. 9 through Oct. 12, has been linked to three deaths. It affected more than 700,000 Californians in 35 counties and cost residents, businesses and the public sector over $2 billion dollars.
The blackout, the seventh one scheduled this year, impacted 39 hospitals, too.
For those reasons and more, the recent massive, pre-planned Pacific Gas and Electric (PG&E) blackout two weeks ago in California, the wealthiest state in the nation, was not only upsetting to most people, but also hard to accept and widely criticized.
PG&E resorted to cutting power in designated areas of the state because the National Weather Service predicted heavy winds, high temperatures and dry air, conditions that the company feared would lead to disastrous wildfires if power lines – many of them supported by aging, worn-out transmission towers – were downed. They could spark, setting the dry vegetation ablaze, which could result in deaths and the destruction of property.
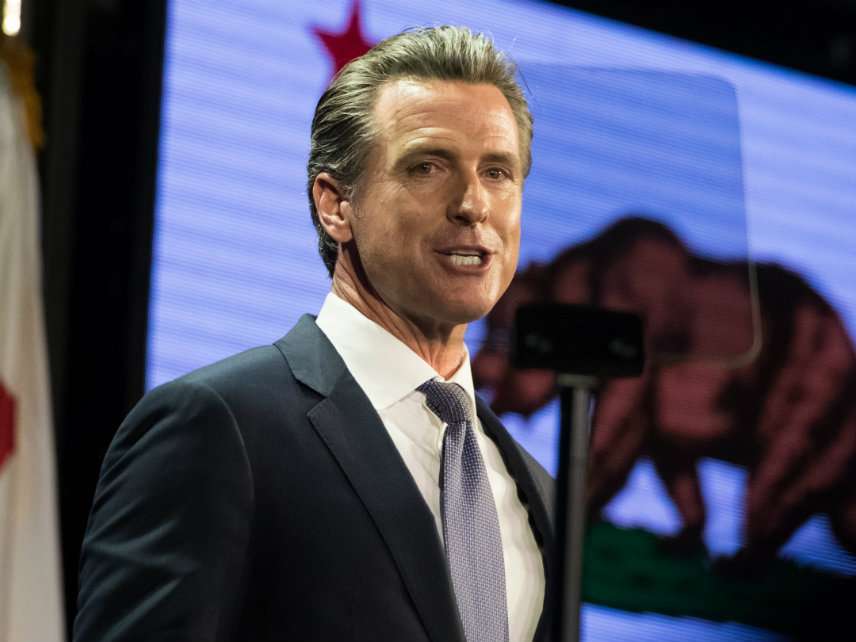
Last week, Gov.Gavin Newsom called the power outage “unacceptable.”
“Californians should not pay the price for decades of PG&E’s greed and neglect,” said Governor Newsom last week, slamming the investor-owned utility. “We will continue to hold PG&E accountable to make radical changes – prioritizing the safety of Californians and modernizing its equipment.”
“For years, PG&E has done a poor job on maintenance and tree clearing, and they’re still not even close to where they need to be,” said Sen. Bill Dodd (D-Napa), whose district was impacted by the blackout. “That fact, along with breakdowns in communication, are unacceptable. Sadly, poor performance by PG&E is par for the course, so it’s not surprising.”
The company is the largest electricity and natural gas power provider in the state serving some 16 million people from Santa Barbara and Kern counties in the South, up north to the Oregon state line, and east to the Nevada and Arizona borders.
Even as the utility company, the largest in the state serving 16 million people, faces sharp criticism from state officials, it is defending its decision to cut power as a safety measure. PG&E also cautions that it may have to schedule rolling blackouts for the next 10 years while it updates equipment.
In a hearing before the California Utilities Commission (CUP) on October 18, PG&E CEO Bill Johnson, along with nine other company executives, admitted the company’s shortcomings during the blackout and apologized for them. They also assured state officials that PG&E is taking measures – including updating its equipment, using technology to limit the target area of future blackouts and trimming trees near transmission towers – to minimize outages and prevent wildfires.
“We recognize the hardship that the recent public safety power shutoff event caused,” Johnson wrote in a letter to the PUC. “At the same time, we ask our customers … to keep in mind that statistic that matters most: there were no catastrophic wildfires.”
PG&E is currently facing a number of uphill battles in California.
The utility provider is taking steps to emerge from bankruptcy after facing more than $30 billion in liabilities for wildfires (far more than its total revenue in 2017, which was $17.4 billion). The worst was last year’s Camp Fire, the deadliest in the state’s history, which resulted in the deaths of 86 people, gutted more than 18,000 buildings and ravaged more than 150,000 acres of land, including the town of Paradise in Butte County.
Critics are also blasting the utility company for the way it handled not only the disruption of service but also its customer service response and public relations activity related to the blackout.
“You guys failed on so many levels on pretty simple stuff,” said Marybel Batjer, president of the California Public Utilities Commission, pointing out that the company’s website, which many of its customers were relying on for information pertaining to the blackouts, crashed.
Tanu Henry, California Black Media



 Activism4 weeks ago
Activism4 weeks ago
 Business4 weeks ago
Business4 weeks ago
 Activism4 weeks ago
Activism4 weeks ago
 Arts and Culture4 weeks ago
Arts and Culture4 weeks ago
 Activism4 weeks ago
Activism4 weeks ago
 Activism4 weeks ago
Activism4 weeks ago
 Alameda County4 weeks ago
Alameda County4 weeks ago
 Activism4 weeks ago
Activism4 weeks ago