#NNPA BlackPress
California State Bar Shaken by Personnel Issues Involving Two Black Women

In less than one month, the State Bar of California has been roiled in high-level personnel snafus involving two prominent Black California women.
In July, the California State Bar offered Fredericka McGee, a respected California legislative attorney, the position of executive director. Then, in August, the organization which serves as an administrative arm of the State Supreme Court and is charged with protecting the public interest, reportedly rescinded that offer without an explanation. McGee has been a licensed attorney with the Bar for almost 30 years.
Then, last week, Debbie Manning, a member of State Bar’s 13-member board — the only African American serving on the governing body — abruptly resigned midway through her term. Manning was appointed to a four-year term by the state Senate in 2018.
Manning, a “non-attorney” member, was appointed to a four-year term by the State Senate in 2018. Previously, Manning was not only the first Black woman to join the Legislature’s Office of the Senate Sergeant-at-Arms in 1977, she was also the first woman to serve as Senate Chief Sergeant-at-Arms. She held that position from 2014 until 2017.
Manning’s resignation came just one week after the Bar met to discuss the hiring of the next executive director with extended public comment in support of McGee after which the board went into closed session but did not report any decision or action. Manning did not give a reason for leaving.
Powerful Support: State Leaders Defend McGee at Board Meeting
At the Friday, Sept. 4 State Bar public board meeting, supporters urged the body to reconsider its decision and renegotiate with McGee for the executive director position. That meeting was delayed when an individual wrote the “n” word several times and other profanity directed toward Black people in the Zoom meeting chatbox, which caused the meeting to be delayed for almost an hour.
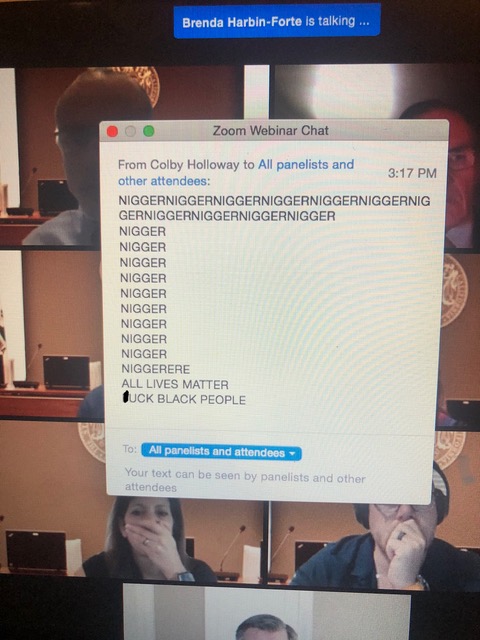
Screenshot of the State Bar Zoom Board meeting September 4, 2020
Despite the delay, a diverse group of people spoke at the meeting in support McGee — supporters say a testament to her rapport with lawmakers; attorneys of all colors and backgrounds; business leaders; members of the African American community; leaders in major service organizations, and more. Among them were representatives of the California Association of Black Lawyers, SEIU, Planned Parenthood and the ACLU.
Assemblymember Shirley Weber (D-San Diego), speaking on behalf of the California Legislative Black Caucus (CLBC), was the first speaker to address the board of trustees.
Weber said, speaking on accounts of published reports, that McGee’s situation is one of the reasons the CLBC talks about the “increase of representation of people of color, particularly African Americans in all aspects.”
Weber said the Bar’s alleged withdrawal “brought tremendous concern” to members of the CLBC.
“(McGee) had accepted the position, was making efforts to move, change her residency, and basically move around for this position, and then all of sudden the position was withdrawn,” Weber said. “We stand united in requesting that you provide the state bar the best leader as possible, as we’ve always found that to be of the character and qualifications of Ms. Fredericka McGee.”
In closing, Weber referenced the constitutional relationship between the Legislature and the State Bar. The Legislature annually authorizes a “fee bill” to allow the Bar to assess lawyers’ licensing fees, according to Ed Howard, a Sacramento public interest lobbyist and long-time State Bar watcher.
A History of Turmoil and Mismanagement
Over the years, the State Bar has been under scrutiny for some of its practices and the way its leaders have managed the organization. In 1998, then Gov. Pete Wilson vetoed a bill that would’ve authorized the agency to charge lawyers in the state annual licensing fees to fund the Bar.
A layoff of two-thirds of the Bar’s staff members was hanging in the balance and the group’s attorney discipline system temporarily shut down for lack of funds. Those issues were only resolved in 1998 after the state’s Supreme Court intervened.
Gov. Arnold Schwarzenegger’s administration vetoed another fee authorization bill, Senate Bill 641, in 2009. Schwarzenegger justified his action by basing it on a state audit that discovered irregularities in enforcing attorney discipline, embezzlement of $675,000 by a former employee, and prohibited disclosure of the rating of a potential candidate for the appellate bench.
In a written message, the governor said the Bar’s scandals “cannot continue with business as usual.”
“As the organization charged with regulating the professional conduct of its members, the conduct of the State Bar itself must be above reproach,” Schwarzenegger stated. “Regrettably, it is not.”
In 2016, after the California Legislature did not pass a Bar dues bill, and the state’s Supreme Court had to step in to authorize the agency to collect interim dues. The American Bar Association reported on Nov. 16, 2016, that both Legislative houses were at odds about the bar’s “reform measures,” introduced by the Assembly. The issue was about a study of whether the bar should break into two parts, splitting the Bar’s attorney discipline abilities from its trade organization tasks.
Last month, the Assembly and the Senate passed Assembly Bill (AB) 3362, a bill that would again authorize the Bar to collect fees from California attorneys and restrict its board of trustees from discussing issues about the Bar’s exams administration in seclusion. At the moment, Gov. Gavin Newsom is reviewing the bill.
At the September 4th board meeting, Fabian Núñez, a former Assemblymember, who represented the 46th District in Los Angeles County and served as speaker of the Assembly from 2004 to 2008, highlighted McGee’s professionalism and praised her “level of dignity,” depth of knowledge,” ability to “build relationships,” and “certainty of purpose.”
Núñez said that within his nearly five-year tenure, McGee was his general counsel and he watched her juggle and manage legal matters of the Assembly, the rules committee, and judiciary issues.
“It’s something unmatched in California,” Núñez said of McGee’s skill set. “Quite frankly, it’s unique because she also possesses the skills that are so important when you are managing a large organization such as the State Bar.”
Gov. Newsom’s former Legislative Affairs Secretary, Anthony Williams also said in support of McGee, “When I heard that she was a candidate for the executive director for the State Bar, I was pleased and proud not only as a lawyer but also as a Californian who knows the important role that the State Bar plays in public protection and administration of justice. Fredericka understands that. I hope that you reconsider it, such a sensitive, personnel decision,” Williams said.
The board of trustees’ duties includes developing the guiding policies and principles of the Bar. It comprises five lawyers appointed by the California Supreme Court, two lawyers appointed by the legislature, and six non-attorney members (four named by the governor).
The State Bar’s Board of Trustees Responds
The governing body’s chairperson Alan Steinbrecher pointed out that the makeup of the state bar is one of diversity and inclusion and at the end of the meeting sought to provide examples of two prior African American State Bar executive directors.
“In my work with the state bar’s leadership team and with staff, I know that the commitment to diversity and inclusion is widely shared throughout the organization,” Steinbrecher said. “As our former executive director said, ‘We want diversity and inclusion to be built in and not built on.’ I also want to note that contrary to some comments we’ve received, the state bar has been previously led by two capable and talented African American women that served as executive directors.”
Leah T. Wilson, another African American woman, served as executive director for two years before she surprised some when she left the role on Jan. 17 of this year.
The Hon. Judy Johnson, also a Black woman, was the State Bar’s executive director from May 2000 to January 2011. Johnson is now a Superior Court Judge for Contra Costa County, first appointed by Gov. Jerry Brown in 2012.
Before entering a closed session, the Bar’s board of trustees addressed the concerns of McGee’s supporters.
“There has been some speculation about a particular candidate who has been considered for the executive director’s position,” Steinbrecher said. “We are not in the position to respond to specifics reported in the press because the executive director’s selection process is a confidential, personnel matter.”
The executive director of the Bar leads the senior management team responsible for various programs. The position requires the executive director to answer to the board of trustees and advance its policies.
McGee was in the process of transitioning out of her role as vice president of California government affairs and operations for the American Beverage Association (ABA). She worked out of ABA’s office in Sacramento.
In addition, McGee is also the founding president of the Black Youth Leadership Project, Inc., a non-profit organization that offers interactive legislative and debate programs to African American high school students throughout California.
Alice Huffman, the President of the California State National Association for the Advancement of Colored People, said in a written statement dated Sept. 3 that McGee “has been recognized for her exemplary service by a multitude of organizations throughout the state and has a stellar reputation in the legislative and legal community.”
“The California NAACP remains ready to stand with the California State Bar as we ensure a fair and transparent legal system at this pivotal time in our country as we address issues of social justice,” Huffman said in a statement “Again, I wholeheartedly support the California State Bar in its efforts to complete the contractual process that started with Ms. McGee.”
#NNPA BlackPress
LIHEAP Funds Released After Weeks of Delay as States and the District Rush to Protect Households from the Cold
BLACKPRESSUSA NEWSWIRE — The federal government has released $3.6 billion in home heating assistance after a delay that left states preparing for the start of winter without the program’s annual funding.

By Stacy M. Brown
Black Press USA Senior National Correspondent
The federal government has released $3.6 billion in home heating assistance after a delay that left states preparing for the start of winter without the program’s annual funding. The Low-Income Home Energy Assistance Program, known as LIHEAP, helps eligible households pay heating and cooling bills. The release follows a shutdown that stretched 43 days and pushed agencies across the country to warn families of possible disruptions.
State officials in Minnesota, Kansas, New York, and Pennsylvania had already issued alerts that the delay could slow the processing of applications or force families to wait until December for help. In Pennsylvania, more than 300,000 households depend on the program each year. Minnesota officials noted that older adults, young children, and people with disabilities face the highest risk as temperatures fall.
The delay also raised concerns among advocates who track household debt tied to rising utility costs. National Energy Assistance Directors Association Executive Director Mark Wolfe said the funds were “essential and long overdue” and added that high arrearages and increased energy prices have strained families seeking help.
Some states faced additional pressure when other services were affected by the shutdown. According to data reviewed by national energy advocates, roughly 68 percent of LIHEAP households also receive nutrition assistance, and the freeze in multiple programs increased the financial burden on low-income residents. Wolfe said families were placed in “an even more precarious situation than usual” as the shutdown stretched into November.
In Maryland, lawmakers urged the Trump administration to release funds after the state recorded its first cold-related death of the season. The Maryland Department of Health reported that a man in his 30s was found outdoors in Frederick County when temperatures dropped. Last winter, the state documented 75 cold-related deaths, the highest number in five years. Rep Kweisi Mfume joined more than 100 House members calling for immediate federal action and said LIHEAP “is not a luxury” for the 100,000 Maryland households that rely on it. He added that seniors and veterans would be placed at risk if the program remained stalled.
Maryland Gov. Wes Moore used $10.1 million in state funds to keep benefits moving, but noted that states cannot routinely replace federal dollars. His administration said families that rely on medical equipment requiring electricity are particularly vulnerable.
The District of Columbia has already mapped out its FY26 LIHEAP structure in documents filed with the federal government. The District’s plan shows that heating assistance, cooling assistance, weatherization, and year-round crisis assistance operate from October 1 through September 30. The District allocates 50 percent of its LIHEAP funds to heating assistance, 10 percent to cooling, 13 percent to year-round crisis assistance, 15 percent to weatherization, and 10 percent to administrative costs. Two percent is used for services that help residents reduce energy needs, including education on reading utility bills and identifying energy waste.
The District’s plan lists a minimum LIHEAP benefit of $200 and a maximum of $1,800 for both heating and cooling assistance. Crisis benefits are provided separately and may reach up to $500 when needed to resolve an emergency. The plan states that a household is considered in crisis if it has been disconnected from energy service, if heating oil is at 5 percent or less of capacity, or if the household has at least $200 owed after the regular benefit is applied.
The District’s filing notes that LIHEAP staff conduct outreach through community meetings, senior housing sites, Advisory Neighborhood Commissions, social media, posters, and mass mailings. The plan confirms that LIHEAP applicants can apply in person, by mail, by email, or through a mobile-friendly online application and that physically disabled residents may request in-home visits.
As agencies nationwide begin distributing the newly released funds, states continue working through large volumes of applications. Wolfe said LIHEAP administrators “have been notified that the award letters have gone out and the states can begin to draw down the funds.”
#NNPA BlackPress
Seven Steps to Help Your Child Build Meaningful Connections
BLACKPRESSUSA NEWSWIRE — Swinging side by side with a friend on the playground. Sharing chalk over bright, colorful sidewalk drawings. Hiding behind a tree during a spirited game of hide-and-seek. These simple moments between children may seem small, but they matter more than we think

By Niyoka McCoy, Ed.D., Chief Learning Officer, Stride/K12
Swinging side by side with a friend on the playground. Sharing chalk over bright, colorful sidewalk drawings. Hiding behind a tree during a spirited game of hide-and-seek. These simple moments between children may seem small, but they matter more than we think: They lay the foundation for some of life’s most important skills.
Through everyday play, young children begin learning essential social and emotional skills like sharing, resolving conflicts, showing empathy, and managing their emotions. These social skills help shape emotional growth and set kids up for long-term success. Socialization in early childhood isn’t just a “nice-to-have”—it’s essential for development.
Yet today, many young children who haven’t yet started school aren’t getting enough consistent, meaningful interaction with peers. Research shows that there’s a decline in active free play and peer socialization when compared to previous generations.
There are many reasons for this. Children who are home with a parent during the day may spend most of their time with adults, limiting opportunities for peer play. Those in daycare or preschool may have restricted free play, and large classrooms can reduce supervision and social coaching. Some children live in rural areas, are homebound due to illness, have full schedules, or rely on screens to fill their playtime. And for some families, finding other families with young children to connect with isn’t easy.
While these challenges can feel significant, opportunities for connection still exist in every community. Families can take simple steps to help children build friendships, create a sense of belonging, and strengthen social skills. Here are some ideas to get started:
- Storytime sessions at libraries or local bookstores
- Community offerings such as parent-child workshops, art, music, gymnastics, swimming, or sports programs
- Weekly events at children’s museums, which may include art projects, music workshops, or science experiments
- Outdoor exploration, where kids can play with peers
- Local parenting groups that organize playdates and group activities
- Volunteer opportunities where children can participate, such as pet adoption events or packing meals at a food bank
- Classes for kids at local businesses, including hardware, grocery, or craft stores
Some of these community activities are free or low-cost and give kids the chance to build friendships and practice social skills. Parents can also model positive social behavior by interacting with other parents and encouraging their children to play with their peers.
These may seem like small moments of connection, but they can have a powerful impact. Every time your child shares a toy, plays make-believe with peers, or races a friend down the slide, they’re not just playing—they’re learning the skills that build confidence, empathy, and lasting friendships. And it’s good for you, too. Creating intentional opportunities for play also helps you strengthen your own network of parents who can support one another as your children grow together.
#NNPA BlackPress
Seven Steps to Help Your Child Build Meaningful Connections
BLACKPRESSUSA NEWSWIRE — Swinging side by side with a friend on the playground. Sharing chalk over bright, colorful sidewalk drawings. Hiding behind a tree during a spirited game of hide-and-seek. These simple moments between children may seem small, but they matter more than we think

By Niyoka McCoy, Ed.D., Chief Learning Officer, Stride/K12
Swinging side by side with a friend on the playground. Sharing chalk over bright, colorful sidewalk drawings. Hiding behind a tree during a spirited game of hide-and-seek. These simple moments between children may seem small, but they matter more than we think: They lay the foundation for some of life’s most important skills.
Through everyday play, young children begin learning essential social and emotional skills like sharing, resolving conflicts, showing empathy, and managing their emotions. These social skills help shape emotional growth and set kids up for long-term success. Socialization in early childhood isn’t just a “nice-to-have”—it’s essential for development.
Yet today, many young children who haven’t yet started school aren’t getting enough consistent, meaningful interaction with peers. Research shows that there’s a decline in active free play and peer socialization when compared to previous generations.
There are many reasons for this. Children who are home with a parent during the day may spend most of their time with adults, limiting opportunities for peer play. Those in daycare or preschool may have restricted free play, and large classrooms can reduce supervision and social coaching. Some children live in rural areas, are homebound due to illness, have full schedules, or rely on screens to fill their playtime. And for some families, finding other families with young children to connect with isn’t easy.
While these challenges can feel significant, opportunities for connection still exist in every community. Families can take simple steps to help children build friendships, create a sense of belonging, and strengthen social skills. Here are some ideas to get started:
- Storytime sessions at libraries or local bookstores
- Community offerings such as parent-child workshops, art, music, gymnastics, swimming, or sports programs
- Weekly events at children’s museums, which may include art projects, music workshops, or science experiments
- Outdoor exploration, where kids can play with peers
- Local parenting groups that organize playdates and group activities
- Volunteer opportunities where children can participate, such as pet adoption events or packing meals at a food bank
- Classes for kids at local businesses, including hardware, grocery, or craft stores
Some of these community activities are free or low-cost and give kids the chance to build friendships and practice social skills. Parents can also model positive social behavior by interacting with other parents and encouraging their children to play with their peers.
These may seem like small moments of connection, but they can have a powerful impact. Every time your child shares a toy, plays make-believe with peers, or races a friend down the slide, they’re not just playing—they’re learning the skills that build confidence, empathy, and lasting friendships. And it’s good for you, too. Creating intentional opportunities for play also helps you strengthen your own network of parents who can support one another as your children grow together.
-

 Activism3 weeks ago
Activism3 weeks agoOakland Post: Week of November 12 – 18, 2025
-

 Activism4 weeks ago
Activism4 weeks agoOakland Post: Week of November 5 – 11, 2025
-

 Activism2 weeks ago
Activism2 weeks agoIN MEMORIAM: William ‘Bill’ Patterson, 94
-

 Activism3 weeks ago
Activism3 weeks agoHow Charles R. Drew University Navigated More Than $20 Million in Fed Cuts – Still Prioritizing Students and Community Health
-

 Bay Area3 weeks ago
Bay Area3 weeks agoNo Justice in the Justice System
-

 #NNPA BlackPress3 weeks ago
#NNPA BlackPress3 weeks agoThe Perfumed Hand of Hypocrisy: Trump Hosted Former Terror Suspect While America Condemns a Muslim Mayor
-

 #NNPA BlackPress2 weeks ago
#NNPA BlackPress2 weeks agoTrump’s Death Threat Rhetoric Sends Nation into Crisis
-

 #NNPA BlackPress4 weeks ago
#NNPA BlackPress4 weeks agoProtecting Pedophiles: The GOP’s Warped Crusade Against Its Own Lies