Black History
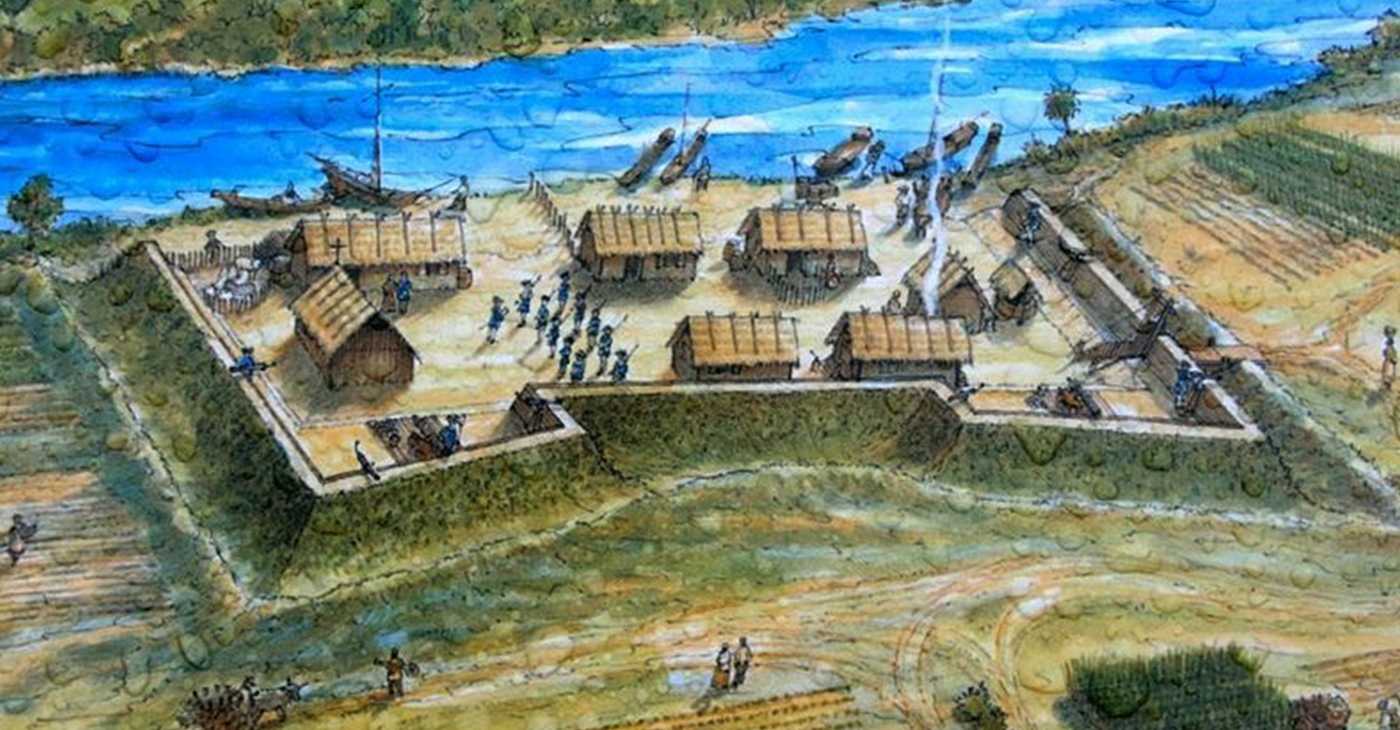
Fort Mose: The First Free Black Settlement
Fort Mose was the first free Black settlement in what is now the United States, and the only one known to have been sponsored by a European colonial government. Two Fort Mose sites eventually existed: one occupied by the Spanish (1737–1740) and the other by Blacks (1752–1763). Although living there was peaceful, the settlement was not immune to violent opposition.

Activism
Oakland Post: Week of February 25 – March 3, 2026
The printed Weekly Edition of the Oakland Post: Week of – February 25 – March 3, 2026
Activism
Oakland Post: Week of February 18 – 24, 2026
The printed Weekly Edition of the Oakland Post: Week of – February 18 – 24, 2026
Activism
Oakland Post: Week of February 11 – 17, 2026
The printed Weekly Edition of the Oakland Post: Week of – February 11 – 17, 2026
-

 Activism4 weeks ago
Activism4 weeks agoCommunity Celebrates Turner Group Construction Company as Collins Drive Becomes Turner Group Drive
-

 Business4 weeks ago
Business4 weeks agoCalifornia Launches Study on Mileage Tax to Potentially Replace Gas Tax as Republicans Push Back
-

 Activism4 weeks ago
Activism4 weeks agoDiscrimination in City Contracts
-

 Arts and Culture4 weeks ago
Arts and Culture4 weeks agoBook Review: Books on Black History and Black Life for Kids
-

 Activism4 weeks ago
Activism4 weeks agoCOMMENTARY: The Biases We Don’t See — Preventing AI-Driven Inequality in Health Care
-

 Activism4 weeks ago
Activism4 weeks agoPost Newspaper Invites NNPA to Join Nationwide Probate Reform Initiative
-

 Alameda County4 weeks ago
Alameda County4 weeks agoBlack History Events in the East Bay
-

 Activism4 weeks ago
Activism4 weeks agoArt of the African Diaspora Celebrates Legacy and Community at Richmond Art Center