World
Italy: UN Presence in Niger, Sudan Can Help Migrant Crisis

Migrants wait to disembark from the Italian Navy vessel ‘Chimera’ in the harbor of Salerno, Italy, Wednesday, April 22, 2015. Italy pressed the European Union on Wednesday to devise concrete, robust steps to stop the deadly tide of migrants on smugglers’ boats in the Mediterranean, including setting up refugee camps in countries bordering Libya. Italian Defense Minister Roberta Pinotti also said human traffickers must be targeted with military intervention. (AP Photo/Francesco Pecoraro)
FRANCES D’EMILIO, Associated Press
ROME (AP) — Italy pressed the EU on Wednesday to devise robust steps to stop the deadly tide of migrants crossing the Mediterranean, including considering military intervention against smugglers and boosting U.N. refugee offices in countries bordering Libya.
“We know where the smugglers keep their boats, where they gather,” said Defense Minister Roberta Pinotti. “The plans for military intervention are there.”
Some 90 percent of smugglers’ boats leave from Libya, where the lack of a central authority coupled with extremists affiliated with the Islamic State group have contributed to chaos and lawlessness that have allowed criminal trafficking networks to proliferate.
Pinotti said Italy was willing to take the helm of any military intervention if asked and as long as it is carried out as an international mission, backed by the United Nations.
“We’re ready to do our share,” she told Sky TG24. “We’re the closest country to Libya.”
Pinotti spoke a day before EU leaders hold an emergency summit in Brussels called in the wake of a shipwreck off Libya last weekend that may have killed more than 800 migrants. It would be the highest known loss of migrants’ lives in a single incident in the Mediterranean.
Ahead of the summit, Premier Mario Renzi called for EU leaders to approve three key proposals: doubling the resources and assets of the current EU border patrol mission; destroying smugglers’ boats and improving coordination across the EU for transferring asylum seekers.
“European Union naval operations in the Horn of Africa have successfully fought piracy — and a similar initiative must be developed to effectively fight against human trafficking in the Mediterranean,” Renzi wrote in a New York Times opinion piece. “Trafficking vessels should be put out of operation.”
In the latest arrivals of migrants, an Italian naval vessel docked in the Sicilian port of Augusta with 446 people who had been rescued off the southern coast of the Italian mainland. The navy said 59 were children.
“We prefer to die trying (to migrate) than stay back there and die,” said Emmanual, a Nigerian migrant who recently arrived in Sicily. “Stay at home and get shot dead or maybe burnt to death, I just prefer to die while trying or survive.”
Later in the day, another 540 migrants arrived in Salerno on the mainland. Some were in isolation under a tent of the main deck of the Italian navy ship that rescued them since they had scabies — underscoring a growing health threat that on Wednesday prompted Italian Health Minister Beatrice Lorenzin to convene a summit of EU health ministers in Rome to coordinate immunization and other health measures for the new arrivals.
Pinotti said she was cautiously hopeful that the EU summit on Thursday, solicited by Italy, would take tangible steps to deal with the emergency.
“We think it’s the moment in which Europe decides, forcefully, to have an international police operation, which will undo this band of criminals,” Pinotti said.
In a speech to Parliament, Renzi urged the EU to swiftly craft long-range, comprehensive policy on the migrants.
“When a person has to risk his life because he needs to escape from a situation where they are chopping off the heads of those near him, you cannot discourage departures with a generic statement,” the premier said. “You can do it by putting the (U.N.) High Commissioner for Refugees in Niger, Sudan” and elsewhere in Africa.
Italian media reports this week said Italian government officials were considering proposing the setting up of refugee camps, under U.N. auspices, in Niger, Tunisia and Sudan, so that migrants’ applications for refugee status could be examined there. Renzi didn’t specify if camps would be an option, but stressed involvement of U.N. refugee offices in countries near Libya.
Pinotti indicated that if requests for asylum were processed in Africa, all EU countries could take a share of the migrants found eligible for refugee status or asylum.
She urged “sharing and co-responsibility,” saying the migrants “all can’t arrive in Italy.”
Italy has saved about 200,000 migrant lives at sea since the start of 2014. But Renzi said Italy’s “noble, generous reaction alone isn’t enough.”
“We are asking Europe to be Europe, not just when it’s time to devise a budget,” Renzi said.
He said broad, long-term EU strategy, including wider sea patrols, could help combat “21st-century slave drivers” of migrants. He also called for a robust presence of “international organizations” in the southern part of Libya.
Pinotti warned that the flow of migrants isn’t about to stop, saying “90 percent are from Nigeria, Ethiopia, Somalia, from places where they are afraid of dying. We cannot stop them” from leaving their homelands.
Mohammed Cisse, a recent migrant from Gambia, said he and his “blood brothers” have little choice but to leave.
“We are all from the same Africa, we are risking our lives to cross the sea to come to Europe,” he said from Clatagirone, Sicily. “It’s very painful, we are dying at sea.”
Since Italy is the first EU country where the boat migrants set foot, they stay in reception centers, sometimes for years, while their requests or appeals for asylum are processed.
Migrants deemed ineligible for asylum are ordered expelled, but many slip away and head to northern Europe to reach relatives.
Copyright 2015 The Associated Press. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten or redistributed.
Activism
Newsom, Pelosi Welcome Election of First American Pope; Call for Unity and Compassion
“In his first address, he reminded us that God loves each and every person,” said Newsom. “We trust that he will shepherd us through the best of the Church’s teachings: to respect human dignity, care for the poor, and wish for the common good of us all.” Newsom also expressed hope that the pontiff’s leadership would serve as a unifying force in a time of global instability.

By Bo Tefu, California Black Media
Gov. Gavin Newsom and First Partner Jennifer Siebel Newsom on May 8 issued a statement congratulating Pope Leo XIV on his historic election as the first American to lead the Catholic Church.
The announcement has drawn widespread reaction from U.S. leaders, including former House Speaker Nancy Pelosi, who called the moment spiritually significant and aligned with the values of service and social justice.
In their statement, the Newsoms expressed hope that the newly elected pope would guide the Church with a focus on compassion, dignity, and care for the most vulnerable. Newsom said he and the First Partner joined others around the world in celebrating the milestone and were encouraged by the pope’s first message.
“In his first address, he reminded us that God loves each and every person,” said Newsom. “We trust that he will shepherd us through the best of the Church’s teachings: to respect human dignity, care for the poor, and wish for the common good of us all.”
Newsom also expressed hope that the pontiff’s leadership would serve as a unifying force in a time of global instability.
“May he remind us that our better angels are not far away — they’re always within us, waiting to be heard,” he said.
Pelosi, a devout Catholic, also welcomed the pope’s election and noted his symbolic connection to earlier church leaders who championed workers’ rights and social equality.
“It is heartening that His Holiness continued the blessing that Pope Francis gave on Easter Sunday: ‘God loves everyone. Evil will not prevail,’” said Pelosi.
Activism
Retired Bay Area Journalist Finds Success in Paris with Black History Tours
In the late 90s, Stevenson finally realized her dream of living in Paris, now with her daughter. She started exploring the history of Africans in the city and would go on to teach others the same. Her business, which she named Black Paris Tours (BPT), received a significant boost when a family friend gave her a stack of cash and encouraged her to expand on the knowledge that she had only started to share with people she knew.
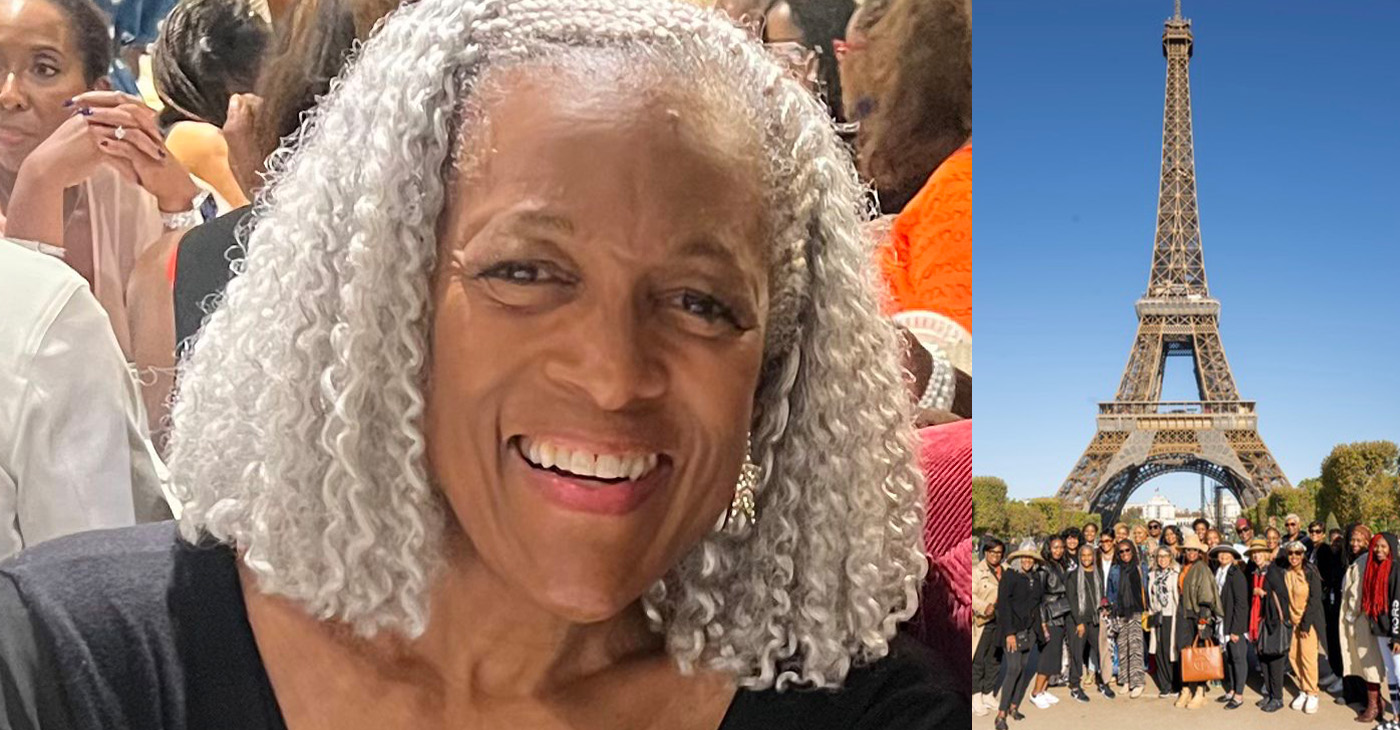

By Post Staff
There were two things Oakland-born, East Palo Alto-raised Ricki Stevenson always dreamed of:
- Going to New York as a newscaster to tell the true story of Blacks in America.
- Living and working in Paris one day.
Her dreams of life in Paris began when she was three years old and her mother, a former professional dancer, took her to see Josephine Baker perform. She was 11 when her parents took her to the Stanford University campus to meet James Baldwin, who was speaking about his book, “The Fire Next Time.” Ricki says that’s when she knew she’d one day live in Paris, “the city of light!”
But before that would ever happen, she had a tumultuous career as a newscaster across the country that was inspired by her family’s history.
Stevenson recalls marching with Cesar Chavez as he fought for labor rights for farm workers in California.
“Are we Mexican too?” she asked her parents. “No, but we will fight for everyone’s human rights,” they responded to her.
Ironically, Ricki’s paternal family roots went back to Greenwood, Oklahoma, infamous for the 1921 bombing of Black Wall Street. A time when Black people had oil wells, banks, and a thriving business community.
This background would propel her into a 25-year journalism career that gave her the opportunity to interview greats like President Jimmy Carter, PLO leader Yassir Arafat, James Baldwin, Rev. Jesse Jackson, UN Ambassador Andrew Young, Miriam Makeba, and the leaders of South African liberation movements.
A job offer from KCBS radio brought her back to the Bay Area in the 1980s. Then came the switch to TV when she was hired as a Silicon Valley business reporter with KSTS TV, working at the first Black-owned television station in northern CA (created and owned by John Douglas). Along the way, Stevenson worked as an entertainment reporter with BET; coproduced, with her disc jockey brother Isaac, a Bay Area show called “Magic Number Video;” lived in Saudi Arabia; worked as an international travel reporter with News Travel Network; and worked at KRON TV a news anchor and talk show host.
In 1997, Stevenson realized her dream of living in Paris with her young daughter, Dedie. She started exploring the history of Africans in the city and would go on to teach others the same. Her business, which she named Black Paris Tours (BPT), received a significant boost when a family friend, Admiral Robert Toney put a chunk of money in her hand. He said, “Ricki, my wife and I have been coming to Paris for 20 years, but in just two days with you and Dedie, we’ve learned and seen more than we ever did before.”
Years after BPT took off, Ricki met Nawo Carol Crawford and Miguel Overton Guerra, who she recruited as senior scholar guides for Black Paris Tours.
Guerra says he is proud of his work with Black Paris Tours in that it provides a wealth of information about the rich legacy of African and African American history and influence in Paris and Europe.
“I tend to have a feeling for history always being a means of a reference point backwards … you start to understand the history, that it isn’t just the United States, that it began with African people,” Guerra says.
He said that it’s been a pleasure to watch people learn something they didn’t know before and to take them through the city to key points in Black history, like hangout spots for writers like Baldwin and Richard Wright, restaurants in the busiest parts of Paris, the home of Josephine Baker and so much more.
Although the tours are open to all, Guerra hopes that those of African descent from all over the world can embrace that they don’t have to just stay where they are because movies and media have portrayed cities like Paris to be only white, it’s multicultural and accepting to all.
“We’ve been here, and we’ve been there, going way back when. And we shouldn’t be considered or consider ourselves to be strangers in any place that we go to,” he said.
Stevenson notes they’ve had 150,000 people take their tour over the years, with notables like former NFL quarterback Colin Kaepernick, Smokey Robinson, Steve Harvey, Miriam Makeba, and more.
Friends and former media colleagues of Stevenson compliment the BPT crew on their knowledge of the city and their ability to always keep it interesting.
“He [Guerra] just had a deep, deep wealth of knowledge and he was constantly supplanting information with historical facts and the like. I love that it was demonstrating and showing how Black people have thrived in Paris or contributed to the culture in Paris,” Candice Francis said.
She toured in the summer of 2022 and stated that in the two weeks that they visited Paris, BPT was the highlight of her trip. She shared that she was proud of Stevenson and the life she’d managed to manifest and build for herself.
“Even if you’re visiting Paris for the tenth time, if you haven’t taken the tour, then by all means, take it,” Francis emphasized.
Magaly Muñoz, Gay Plair and Paul Cobb also contributed to this story. You can book your own adventure with Black Paris Tours at www.blackparistour.com.
Activism
COMMENTARY: Will a Dictator’s Loss Change Trump’s Tune?
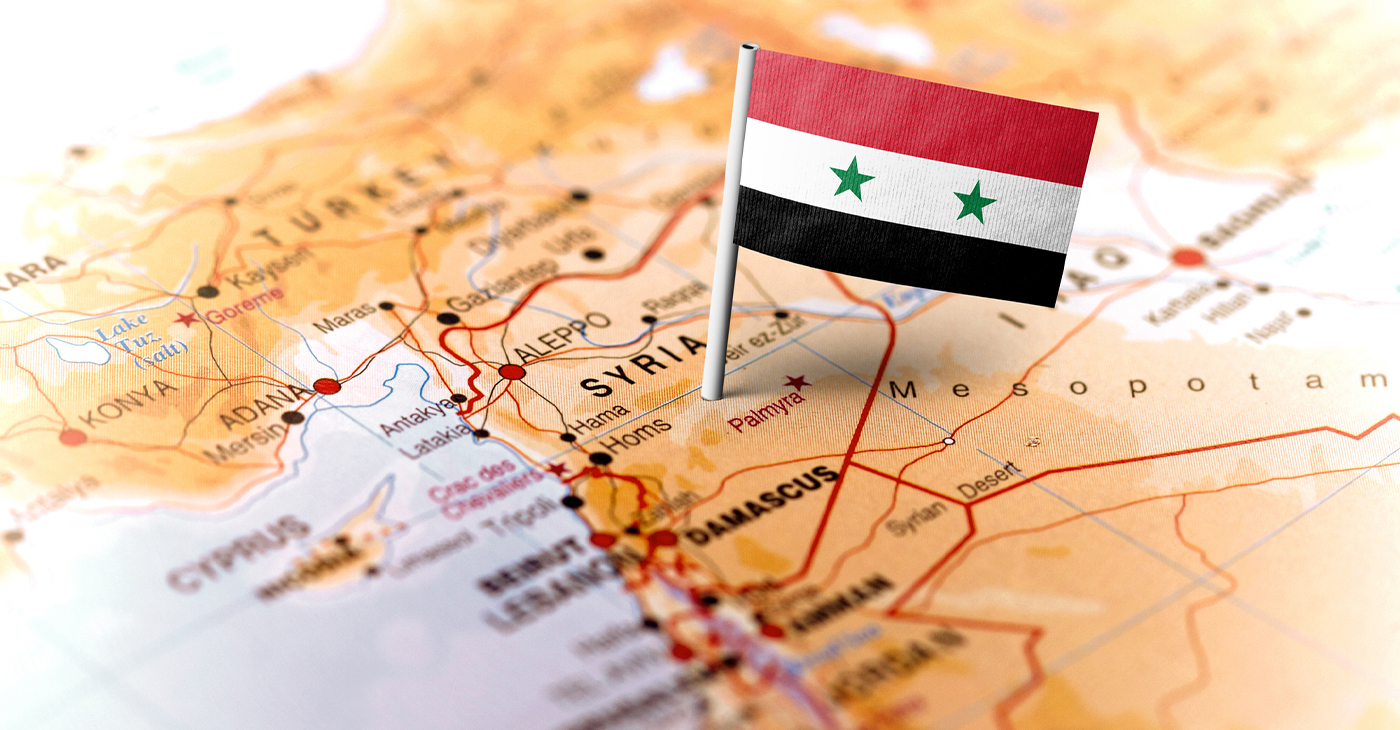
What’s happened in Syria has the potential of reshaping the politics of the entire Middle East. The U.S. can’t afford to sit back and do nothing. Now is the time to exert peaceful, diplomatic influence on how Syria maintains stability and goes forward with a new democracy.
By Emil Guillermo
In our polarized country, half of America can’t wait, while many of us still wonder, “where’s Kamala?”
I hope President-elect Trump — who famously said during the campaign that he’d be a dictator on day one — eats his words.
Dictators aren’t doing so well these days.
Last weekend, the dictator Bashar al-Assad was run out of Syria and sought exile with his puppet master/dictator Vladimir Putin of Russia. In just about two weeks, a coalition of rebels applied enough pressure to end a family regime in Syria that lasted 50 years.
al-Assad’s wealthy family dictatorship plundered Syria and ruled in terror.
It sounds all too familiar to Filipino Americans, many of whom came to the U.S. fleeing the Philippine dictator Ferdinand Marcos.
al-Assad’s end was different from the Filipinos who forged a peaceful People Power movement that chased the Marcos family to Hawaii where they sought refuge from their U.S. puppet handlers.
But as in Manila, there was cheering on the streets of Syria. Men, women, and children. Christian, Muslims, different sects and ethnicities, all united against al-Assad.
al-Assad has been described as a genocidal narco-trafficking tyrant, whose friends were America’s biggest enemies, Iran, Hezbollah, and Russia, said Mouaz Moustafa, the executive director of the Syrian Emergency Task Force, on CNN.
Moustafa said it was amazing that there would be no more Russian airstrikes, no more al-Assad gulags torturing civilians. “To see good triumph over evil is an amazing thing,” he added.
But last weekend has some trickle down.
Consider that we are talking about al-Assad, the one Tulsi Gabbard consorted with and hyped to her colleagues when she was in Congress. Now Assad has been shamed into exile with his puppet master Russia, and Gabbard wants to be the U.S. director of national security? Given her wrongheaded judgment on al-Assad, can she be trusted with any national secrets?
It’s still not over in Syria, as now there will be a scramble to see what kind of governing democracy emerges.
Predictably, Donald Trump has said, “The United States should have nothing to do with it. This is not our fight. Let it play out. Do not get involved.”
Nouveau isolationism?
What’s happened in Syria has the potential of reshaping the politics of the entire Middle East. The U.S. can’t afford to sit back and do nothing. Now is the time to exert peaceful, diplomatic influence on how Syria maintains stability and goes forward with a new democracy.
Overall, the ouster of the dictator should give Trump pause.
If by nominating MAGA loyalists like Gabbard, Pete Hegseth and Kash Patel, Trump’s testing the evolution to strongman rule in the U.S., he should consider what happened before last weekend.
In South Korea, a weak president tried to declare martial law and was voted down by Parliament. That’s a faux strongman.
Let’s hope Trump learns a lesson from the week’s news.
The next president sets the tone for a politics that’s already toxic.
He needs to remember the joy in Syria this week when an autocrat was dumped in the name of freedom and democracy.
About the Author
Emil Guillermo is an award-winning Bay Area journalist. His commentaries are on YouTube.com/@emilamok1. Or join him at www.patreon.com/emilamok
-

 Activism4 weeks ago
Activism4 weeks agoAI Is Reshaping Black Healthcare: Promise, Peril, and the Push for Improved Results in California
-

 Activism4 weeks ago
Activism4 weeks agoBarbara Lee Accepts Victory With “Responsibility, Humility and Love”
-

 Activism4 weeks ago
Activism4 weeks agoESSAY: Technology and Medicine, a Primary Care Point of View
-

 Activism4 weeks ago
Activism4 weeks agoFaces Around the Bay: Author Karen Lewis Took the ‘Detour to Straight Street’
-

 Activism4 weeks ago
Activism4 weeks agoNewsom Fights Back as AmeriCorps Shutdown Threatens Vital Services in Black Communities
-

 Arts and Culture4 weeks ago
Arts and Culture4 weeks agoBOOK REVIEW: Love, Rita: An American Story of Sisterhood, Joy, Loss, and Legacy
-

 #NNPA BlackPress4 weeks ago
#NNPA BlackPress4 weeks agoThe RESISTANCE – FREEDOM NOW
-

 Alameda County4 weeks ago
Alameda County4 weeks agoOUSD Supt. Chief Kyla Johnson-Trammell to Step Down on July 1


















































