Bay Area
Among the Reasons COVID-19 is Worse for Black Communities: Police Violence

There are various reasons COVID-19 is killing Black people at six times the rate of white people, including a lack of access to health care, and poor environmental conditions in Black communities.
But one largely unexamined contributor to the disparity, according to a panel of UC Berkeley experts, is the trauma and stress caused by police violence in those communities, and the physical toll of that violence.
“There are levels of chronic stress associated with living in an environment that has more police violence, and the threat of that force on its residents,” said Denise Herd, a professor at the School of Public Health who recently examined how that stress can lead to disease in her paper “Cycles of Threat: Graham V. Connor, Police Violence and African American Health Inequities,” which will be published in an upcoming issue of the Boston University Law Review.
With the world still in the grips of the pandemic, there is no specific research relating COVID-19 cases to police violence, but Herd said the connection between the chronic stress caused by persistent police-related trauma, and diseases like asthma, diabetes, hypertension and heart disease, which has led to COVID-19 mortality, is clear.
“Those mental health issues often go untreated in African American communities and can lead to diseases that make them more compromised to COVID-19,” she added.
Another potentially complicating factor is that asking Black people, especially Black men, to wear masks, as many public health authorities are requiring, may invite unwarranted attention from police, who have falsely profiled Black men as criminals.
“It’s a corollary to the ‘hoodie’ argument from a few years ago, where it is not uncommon for racial minorities wearing hoodies to be considered a threat, while others freely wear them without fear of harassment,” said Osagie Obasogie, a Berkeley professor of bioethics.
“Everyday racism continues to be a more immediate concern to communities of color than a pandemic, so some people may decline to wear masks,” he added.
‘Two Americas, two epidemics’
Herd, who is also associate director of Berkeley’s Othering and Belonging Institute, pointed to an array of studies showing Black people are more likely to face poor treatment from law enforcement that includes being stopped, injured or even killed by police.
One study, conducted from 2001 to 2014, analyzed 683,000 injuries caused by police that prompted treatment in emergency rooms across the country. The data found that Black people were nearly five times more likely to experience police-related injuries than white people, and they also experienced a mortality rate from those injuries twice as high as white patients.
Moreover, Herd said the use of so-called Terry stops, or stop-and-frisk policies, that allow police officers to question, search or detain people they suspect are involved in criminal activity, have been used as a way to hyper-police Black communities, creating chronic stress that lowers a person’s resistance to disease.
Herd referenced data from the New York Civil Liberties Union that showed between 2004 and 2012, four million Terry stops were conducted predominantly on Black and Latino pedestrians. In 2011 alone, 90% of pedestrians stopped were either Black or Latino, and 20% of the time police used physical force.
Another study found that men who reported a high number of police stops in their lifetimes were also three times more likely to exhibit post-traumatic stress disorder symptoms and high levels of anxiety and stress.
There isn’t just one reason for the health problems in these communities, said Herd. Access to green spaces, affordable housing and other economic factors also play a role. But forms of discrimination and unfair treatment by law enforcement are linked with higher rates of disease in Black communities, she said.
In her paper, Herd pointed to research showing that in neighborhoods where pedestrians were more likely to be questioned by police, there was a prevalence of high blood pressure, diabetes, asthma and obesity; health outcomes proven to cause severe COVID-19 symptoms in patients infected with the disease.
“We don’t have all the data in yet, but it looks like it’s two Americas, two epidemics,” said Herd. “In the profile that we saw with affluent white people who had the disease first, it was because of international travel, and the cases tended to be within the older population. I don’t think that’s going to be true for the African American population. We do also see younger African American people dying.”
Wearing a face mask while Black
While wearing a face mask in public to stop the spread of COVID-19 may seem like common sense for some, for people of color, particularly Black men, wearing or not wearing a mask while out can be a double-edged sword.
Erin Kerrison, an assistant professor at Berkeley’s social welfare school who studies how law and legal institutions operate as social determinants of health, said that because of the distrust Black people have toward law enforcement, they may not wear masks in public to avoid being viewed as criminals.
“Due to the psychological harm and damage done in those stop-and-frisk encounters, and often the unwarranted harassment, there is a feeling that the police treat them as guilty until proven innocent,” Kerrison said.
For example, following the 2012 shooting and killing of Trayvon Martin, a young Black teenager walking around his Florida neighborhood, some people said the killing was justified because “he looked shady,” Kerrison said.
“What law enforcement views as a public-safety threat is deeply racialized,” said Kerrison. “So, it is a common practice for Black citizens to limit, if not altogether avoid, any sort of trigger that would lead to an encounter with a police officer.”
This Friday, Herd and Obasogie, along with other Berkeley public health experts, will host a live Berkeley Conversations video event, “Straight Talk: A Conversation about Racism, Health Inequities, and COVID-19.” It will be co-sponsored by the Othering and Belonging Institute and the School of Public Health.
Although she will not be present at the virtual event, Kerrison said she hopes the conversation extends the dialogue around the unique impact COVID-19 is having on communities of color.
“What’s important is to make sure the fullest truth does get out to as many people that will listen,” she said.
Activism
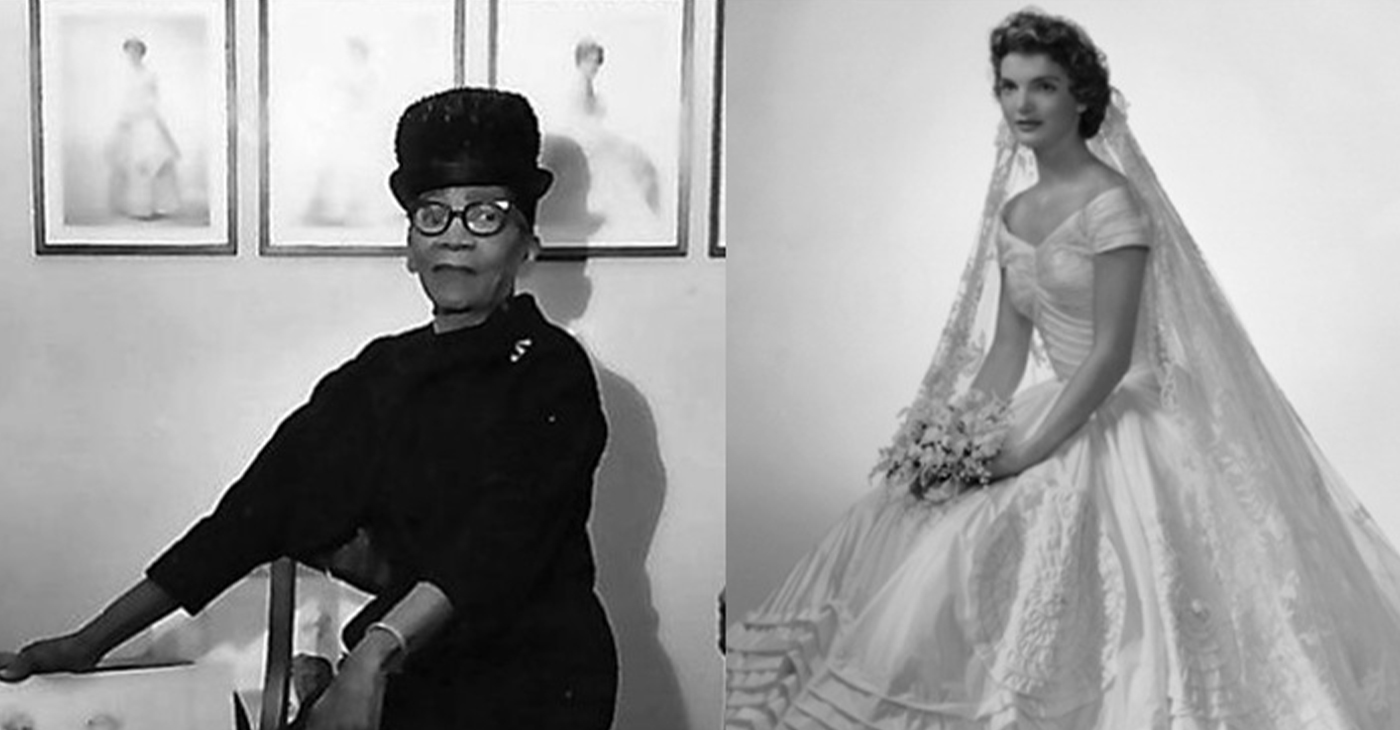
Ann Lowe: The Quiet Genius of American Couture
Lowe was born in Clayton, Alabama, into a family of gifted seamstresses. Her mother and grandmother were well-known dressmakers who created exquisite gowns for women in the area. By the time Lowe was a young girl, she was already showing extraordinary talent — cutting, sewing, and decorating fabric with a skill that far exceeded her age. When her mother died unexpectedly, Lowe – only 16 years old then – took over her mother’s sewing business, completing all the orders herself.

By Tamara Shiloh
Ann Cole Lowe, born Dec.14, 1898, was a pioneering American fashion designer whose extraordinary talent shaped some of the most widely recognized and celebrated gowns in U.S. history.
Although she designed dresses for society’s wealthiest families and created masterpieces worn at historic events, Lowe spent much of her life in the shadows — uncredited, underpaid, yet unmatched in skill. Today, she is celebrated as one of the first nationally recognized African American fashion designers and a true visionary in American couture.
Lowe was born in Clayton, Alabama, into a family of gifted seamstresses. Her mother and grandmother were well-known dressmakers who created exquisite gowns for women in the area. By the time Lowe was a young girl, she was already showing extraordinary talent — cutting, sewing, and decorating fabric with a skill that far exceeded her age. When her mother died unexpectedly, Lowe – only 16 years old then – took over her mother’s sewing business, completing all the orders herself. This early responsibility would prepare her for a lifetime of professional excellence.
In 1917, Lowe moved to New York City to study at the S.T. Taylor Design School. Although she was segregated from White students and forced to work separately, she, of course, excelled, graduating earlier than expected. Her instructors quickly recognized that her abilities were far above the typical student, especially her skill in hand-sewing, applique, and intricate floral embellishment – techniques that would become her signature.
Throughout the 1920s and 1930s, she designed gowns for high-society women in Florida and New York, operating boutiques and working for prestigious department stores. Her reputation for craftsmanship, originality, and elegance grew increasingly. She was known for creating gowns that moved beautifully, featured delicate hand-made flowers, and looked sculpted rather than sewn. Many wealthy clients specifically requested “an Ann Lowe gown” for weddings, balls, and galas.
Her most famous creation came in 1953: the wedding gown worn by Jacqueline Bouvier when she married Massachusetts Sen. John F. Kennedy. The dress – crafted from ivory silk taffeta with dozens of tiny, pleated rosettes – became one of the most photographed bridal gowns in American history. Despite this achievement, Lowe received no public credit at the time. When a flood destroyed her completed gowns 10 days before the wedding, she and her seamstresses worked day and night to remake everything – at her own expense. Her dedication and perfectionism never wavered.
She eventually opened “Ann Lowe Originals,” her own salon on New York’s Madison Avenue. She served clients such as the Rockefellers, DuPonts, Vanderbilts, and actresses like Olivia de Havilland. Yet even with her wealthy clientele, she struggled financially, often undercharging because she wanted every dress to be perfect, even if it meant losing money.
Lowe’s contributions were finally recognized later in life. Today, her exquisite gowns are preserved in museums, including the Smithsonian National Museum of African American History and Culture and the Metropolitan Museum of Art.
In the last five years of her life, Lowe lived with her daughter Ruth in Queens, N.Y. She died at her daughter’s home on Feb. 25, 1981, at the age of 82, after an extended illness.
Activism
BRIDGE Housing President and CEO Ken Lombard Scores Top Honors for Affordable Housing Leadership
The Development Company of the Year honor represents a milestone for BRIDGE Housing, which received the Gold award—its top designation—in a category that included both affordable and market-rate developers. The recognition caps what has been one of the strongest growth periods in the organization’s 42-year history.

By the Oakland Post Staff
San Francisco-based BRIDGE Housing and its president and CEO, Ken Lombard, have been named among the nation’s housing industry standouts, earning two of the top prizes at the 2025 Multi-Housing News Excellence Awards.
BRIDGE Housing was named Development Company of the Year, while Lombard received Executive of the Year, recognition that places the nonprofit affordable housing provider alongside leading national developers of both affordable and market-rate housing.
The awards were announced in New York for the accomplishments achieved during 2024.
Multi-Housing News is one of the industry’s most respected publications. Award winners are selected by a panel of housing professionals, including multifamily developers, architects, and owners.
“BRIDGE Housing is deeply honored to be recognized by Multi-Housing News and our industry peers,” Lombard said. “These awards are a testament to the high-impact, mission-driven work by BRIDGE’s exceptional team to deliver quality affordable housing and support services that empower residents to improve their lives.”
The Development Company of the Year honor represents a milestone for BRIDGE Housing, which received the Gold award—its top designation—in a category that included both affordable and market-rate developers. The recognition caps what has been one of the strongest growth periods in the organization’s 42-year history.
In 2024, BRIDGE significantly expanded its footprint across California, Oregon, and Washington. That momentum continued into 2025, with portfolio growth of 9%, including the addition of nine new communities and 1,187 new or acquired affordable housing units. The nonprofit also added three new projects to its development pipeline as it nears a portfolio of 16,000 units.
The growth reflects a broader strategy aimed at accelerating both acquisitions and ground-up development, supported by partnerships with major financial institutions and innovative capital markets strategies. BRIDGE has also emphasized high-quality design and deep community engagement as central elements of its approach.
BRIDGE became the first affordable housing developer to issue tax-exempt construction bonds for one of the largest affordable housing projects in Portland, Ore., leveraging its strong credit rating.
Earlier this year, the nonprofit launched the BRIDGE Housing Impact Fund, with a goal of investing $1 billion to preserve and create affordable housing. It also closed on $175 million in taxable general-obligation bonds after increasing the offering in response to strong investor demand.
The company’s performance also underscores the role of Lombard, who has led BRIDGE since 2021 and was honored individually for his leadership.
Under Lombard’s tenure, BRIDGE has built a new leadership team with experience drawn from both the nonprofit and private sectors, with a particular focus on what the organization describes as efforts to “break the status quo,” especially in affordable housing finance. Those initiatives have helped reduce capital and construction costs, strengthen relationships with institutional investors, and expand resident support services.
Today, BRIDGE Housing serves more than 33,000 residents across 139 communities on the West Coast.
“Ken has dedicated his career to innovative real estate solutions that improve the quality of life in underserved neighborhoods,” said Kenneth Novack, chair of BRIDGE Housing’s board of directors. “His visionary leadership and the work of our incredible team have positioned BRIDGE for long-term growth that will extend our impact throughout the West Coast.”
Founded in 1983, BRIDGE Housing has helped create more than 23,000 affordable homes with a total development cost of $6 billion.
Activism
Oakland School Board Grapples with Potential $100 Million Shortfall Next Year
The school board approved Superintendent Denise Saddler’s plan for major cuts to schools and the district office, but they are still trying to avoid outside pressure to close flatland schools.

By Post Staff
The Oakland Board of Education is continuing to grapple with a massive $100 million shortfall next year, which represents about 20% of the district’s general fund budget.
The school board approved Superintendent Denise Saddler’s plan for major cuts to schools and the district office, but they are still trying to avoid outside pressure to close flatland schools.
Without cuts, OUSD is under threat of being taken over by the state. The district only emerged from state receivership in July after 22 years.
“We want to make sure the cuts are away from the kids,” said Kampala Taiz-Rancifer, president of the Oakland Education Association, the teachers’ union. “There are too many things that are important and critical to instruction, to protecting our most vulnerable kids, to safety.”
The school district has been considering different scenarios for budget cuts proposed by the superintendent, including athletics, libraries, clubs, teacher programs, and school security.
The plan approved at Wednesday’s board meeting, which is not yet finalized, is estimated to save around $103 million.
Staff is now looking at decreasing central office staff and cutting extra-curricular budgets, such as for sports and library services. It will also review contracts for outside consultants, limiting classroom supplies and examine the possibility of school closures, which is a popular proposal among state and county officials and privatizers though after decades of Oakland school closures, has been shown to save little if any money.
-

 Activism4 weeks ago
Activism4 weeks agoIN MEMORIAM: William ‘Bill’ Patterson, 94
-

 #NNPA BlackPress3 weeks ago
#NNPA BlackPress3 weeks agoBeyoncé and Jay-Z make rare public appearance with Lewis Hamilton at Las Vegas Grand Prix
-

 Activism3 weeks ago
Activism3 weeks agoOakland Post: Week of November 19 – 25, 2025
-

 #NNPA BlackPress4 weeks ago
#NNPA BlackPress4 weeks agoLewis Hamilton set to start LAST in Saturday Night’s Las Vegas Grand Prix
-

 #NNPA BlackPress2 weeks ago
#NNPA BlackPress2 weeks agoLIHEAP Funds Released After Weeks of Delay as States and the District Rush to Protect Households from the Cold
-

 Alameda County2 weeks ago
Alameda County2 weeks agoSeth Curry Makes Impressive Debut with the Golden State Warriors
-

 Activism3 weeks ago
Activism3 weeks agoOakland Post: Week of November 26 – December 2, 2025
-

 #NNPA BlackPress2 weeks ago
#NNPA BlackPress2 weeks agoSeven Steps to Help Your Child Build Meaningful Connections