If you have a question about COVID-19, email Ask SciCheck, a project of FactCheck.org, at AskSciCheck@FactCheck.org. Tell them you are a reader of the Houston Forward Times. You can read previous Ask SciCheck answers here.
#NNPA BlackPress
Video Distorts Early Coronavirus Research To Promote Baseless Bioweapon Conspiracy Theory
SciCheck Digest Human coronaviruses first identified in the 1960s cause common colds. But a viral video misrepresents early research on common coronaviruses and cites unrelated patents to falsely suggest U.S. scientists created the viruses that cause SARS and COVID-19. The video also is not footage of official testimony before the European […]
The post Video Distorts Early Coronavirus Research To Promote Baseless Bioweapon Conspiracy Theory first appeared on BlackPressUSA.



SciCheck Digest
Human coronaviruses first identified in the 1960s cause common colds. But a viral video misrepresents early research on common coronaviruses and cites unrelated patents to falsely suggest U.S. scientists created the viruses that cause SARS and COVID-19. The video also is not footage of official testimony before the European Parliament.
Full Story
Scientists have been studying coronaviruses, a family of viruses that infect animals and humans, for decades — the first was identified in chickens in the 1930s. In 1968, after the first human coronavirus was identified in 1965, virologists grouped them and named them coronaviruses for their crown-like surface, which also resembles the outermost layer of the sun called the corona (corona is the Latin word for crown).

Seven coronaviruses are known to infect humans — four of them, known as common human coronaviruses (229E, NL63, OC43 and HKU1), generally cause mild to moderate symptoms of a common cold. But coronaviruses got more attention in 2003, after the emergence of SARS-CoV-1, the first coronavirus known to cause a severe respiratory illness in humans, followed by MERS-CoV in 2012, and SARS-CoV-2, which causes COVID-19, in 2019.
Both SARS-CoV-1 and MERS-CoV originated in animals and jumped to humans. Although there is still no proof of how SARS-CoV-2 started, many scientists think the available evidence also points to a zoonotic spillover. If SARS-CoV-2 did escape from a lab in Wuhan, there is a general consensus that it was an accident. A U.S. Intelligence report released in 2021 showed that all agencies agreed that “the virus was not developed as a biological weapon” and “most” said the virus “probably was not genetically engineered,” as we reported.
Yet, in a widely shared video misleadingly presented as testimony to the European Parliament, David Martin, a financial analyst, cited unrelated patents and distorted early research on coronaviruses to falsely suggest that scientists in the U.S. created the viruses that cause SARS and COVID-19 as part of a plot to drive vaccine profits.
“Ladies and gentlemen, this was premeditated domestic terrorism,” he said of the COVID-19 pandemic (mark 19:22). “This is an act of biological and chemical warfare perpetrated on the human race. … [T]his was a financial heist and a financial fraud,” he added — a quote that was later shared in a Twitter post that has been retweeted more than 75,000 times.
Except Martin’s entire argument is bunk. Dr. Susan R. Weiss, a coronavirus researcher at the University of Pennsylvania, told us in a phone interview that his statements are full of inaccuracies and completely distort past coronavirus research.
“There is no basis for any of this,” she said. “It makes no scientific sense.”
Martin has pushed several conspiracy theories about the pandemic. In 2020, he was a central figure in the second “Plandemic” video, which also falsely claimed that the pandemic was planned, as we’ve written.
Not European Parliament Testimony
Part of the appeal of Martin’s video — and lending false legitimacy to his claims — is that at first glance, it appears he is speaking in front of the European Parliament and giving official testimony.
“[C]ant believe my ears, what is being said at the europian union,” a Facebook user said, sharing the video, which shows Martin next to a European Parliament flag in what might look to someone like the European Parliament Hemicycle.
“Must watch: This is the opening presentation by Dr David Martin on the origins of Covid in 1965 & Covid Vaccines in 1990!” a Twitter user wrote. “He speaks in front of the European Parliament International Covid Summit III in Brussels on May 3, 2023. Hear and be shocked..!”
In reality, only five of the 705 members of the European Parliament participated in the event, which took place in a room of the parliament’s building in Brussels, as part of a three-day meeting organized by COVID-19 skeptics and anti-vaccination activists. The five Parliament members have participated in actions opposing COVID-19 vaccines.
Natalie Kontoulis, a press officer for the European Parliament, told us in an email that the meeting “was not an official European Parliament event.” She added, “Members of the Parliament can exercise their mandate freely and bear responsibility for both their activities and their content.”
According to the event’s website, the speaker line-up included some prominent COVID-19 misinformation spreaders, including Dr. Robert Malone, Dr. Pierre Kory, and Dr. Ryan Cole. The event content was turned into a book called “ICS 3 – The Whole Truth” and commercialized — a paperback copy sells for $29.99.
SARS-CoV-2 is New, Not Engineered for 56 Years
During the almost 22-minute video, Martin spins a scientifically impossible story that suggests that SARS-CoV-2 and other viruses are the result of experimentation with common cold coronaviruses that were discovered in the 1960s.
“This is actually something that’s been long in the making,” he said of the COVID-19 pandemic (mark 5:31). “In 1967, the year I was born, we did the first human trials on inoculating people with modified coronavirus. Isn’t that amazing? 56 years ago — the overnight success of a pathogen that’s been 56 years in engineering.”
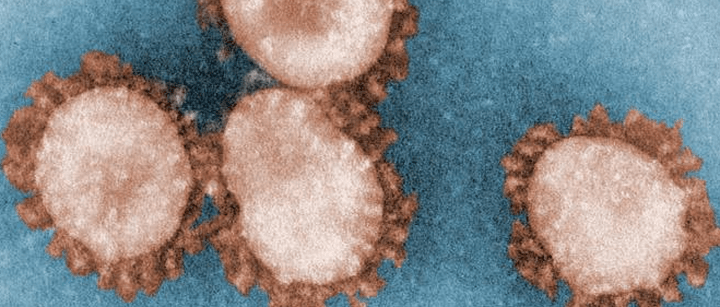
But Martin, who misleads throughout by implying all coronaviruses might be the same, is misrepresenting a study that involved infecting people with a coronavirus that causes a cold. The virus had not been modified. More important, the notion that a common coronavirus could have been manipulated or engineered to create SARS-CoV-2 is incorrect.
“They’re too different,” Weiss said. “We don’t have the ability to turn one into the other.”
About a minute later, he said, “Ironically, the common cold was turned into a chimera in the 1970s. And in 1975, 1976, and 1977 we started figuring out how to modify coronavirus by putting it into different animals, pigs and dogs.”
“That doesn’t make any sense,” Weiss told us.
First, as we said, there are multiple kinds of coronaviruses. Some infect animals and others infect humans — and a few can cross from one species to another one, Weiss told us. “It turns out, the human virus … at least the cold virus, as far as I know, only replicates in humans.” The viruses couldn’t be genetically modified at that time, either, she explained. “We couldn’t engineer viruses at that time,” she said of the 1970s, since the technology to do it, such as cloning, didn’t yet exist.
Martin continues to mislead by saying the inoculation of those supposedly modified common coronaviruses created a huge problem in the pig and dog industry, which led Pfizer to patent its “first spike protein vaccine” in 1990. “Isn’t that fascinating? Isn’t it fascinating that we were, we were told that, ‘Well, the spike protein is a new thing,’” he said (mark 7:44).
Except, that patent was for a canine coronavirus vaccine, which targets an entirely different virus from SARS-CoV-2. In 2020, we debunked related claims that also confused canine coronavirus with the virus that caused the pandemic.
Moreover, scientists have never said that coronavirus spike proteins are “new.” The specific SARS-CoV-2 spike was new, and the genetic sequence was needed to design the vaccines. But one reason why the COVID-19 vaccines could be made so rapidly is because scientists already knew the virus’s spike proteins would be good vaccine targets. The existence of that previous knowledge is not evidence that SARS-CoV-2 was created as a bioweapon or as part of a ploy to sell vaccines.
Martin also falsely claims that SARS-CoV-1 was created in an American lab.
“Are you suggesting that SARS … might have come from a laboratory in the University of North Carolina Chapel Hill? No, I’m not suggesting it. I’m telling you that’s the facts — we engineered SARS,” he said. “SARS is not a naturally occurring phenomenon. The naturally occurring phenomenon is called the common cold … SARS is the research developed by humans weaponizing a life system model to actually attack human beings.”
There is no evidence SARS-CoV-1 was engineered or came from any lab. The virus naturally appeared in 2002 in China, when it likely jumped from civets to humans, and its origins are linked to bats.
Martin pointed to a 2002 patent as supposed proof. But the patent, which is for a method for creating viral vectors, focuses on a pig coronavirus (viral vectors are used to deliver genetic information to cells). As before, the patent is not evidence that the SARS virus was engineered.
Martin also distorted the meaning of a line of the patent that says the method could help produce “an infectious, replication defective, coronavirus particle.”
“Listen to those words: infectious replication defective,” Martin said suggestively (mark 10:18). “What does that phrase actually mean for those of you not familiar with language? Let me unpack it for you. Infectious replication defective means a weapon. It means something meant to target an individual but not have collateral damage to other individuals.”
But he’s wrong again. Replication-defective simply means that a viral particle would be incapable of replicating itself.
Editor’s note: SciCheck’s articles providing accurate health information and correcting health misinformation are made possible by a grant from the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation. The foundation has no control over FactCheck.org’s editorial decisions, and the views expressed in our articles do not necessarily reflect the views of the foundation.
Sources
Payne, Susan. “Family Coronaviridae.” Viruses. 1 Sep 2017.
“Virology: Coronaviruses.” Nature. Vol. 220. 16 Nov 1968.
“Coronavirus: Detailed taxonomy.” AVMA. Accessed 13 Jun 2023.
“Human Coronavirus Types.” CDC. Updated 15 Feb 2020.
“Common Human Coronaviruses.” CDC. Updated 13 Feb 2020.
“Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS).” CDC. 6 Dec 2017.
“Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS).” CDC. Updated 2 Aug 2019
Spencer, Saranac H., et al. “New ‘Plandemic’ Video Peddles Misinformation, Conspiracies.” FactCheck.org. Updated 29 Jun 2021.
Weiss, Susan R. Vice Chair, Department of Microbiology, University of Pennsylvania. Phone interview with FactCheck.org. 5 Jun 2023.
Malone, Robert. “Videos: The International Covid Summit III in the European Parliament, Brussels.” Substack. 15 May 2023.
Alexander, Lorraine K., et al. “An Experimental Model for Dilated Cardiomyopathy after Rabbit Coronavirus Infection.” The Journal of Infectious Diseases. Vol. 166. 1 Nov 1992.
Kontoulis, Natalie. Press officer for the European Parliament. Email sent to FactCheck.org. 9 Jun 2023.
Curtis, Kristopher, et al. “Methods for Producing Recombinant Coronavirus.” International Patent Number WO 02/086068 A2. 31 Oct 2002. Robertson, Lori. “Still No Determination on COVID-19 Origin.” FactCheck.org. 20 Mar 2023.
The post Video Distorts Early Coronavirus Research To Promote Baseless Bioweapon Conspiracy Theory appeared first on Forward Times.
The post Video Distorts Early Coronavirus Research To Promote Baseless Bioweapon Conspiracy Theory first appeared on BlackPressUSA.
#NNPA BlackPress
A Nation in Freefall While the Powerful Feast: Trump Calls Affordability a ‘Con Job’
BLACKPRESSUSA NEWSWIRE — There are seasons in this country when the struggle of ordinary Americans is not merely a condition but a kind of weather that settles over everything.

By Stacy M. Brown
Black Press USA Senior National Correspondent
There are seasons in this country when the struggle of ordinary Americans is not merely a condition but a kind of weather that settles over everything. It enters the grocery aisle, the overdue bill, the rent notice, and the long nights spent calculating how to get through the next week. The latest numbers show that this season has not passed. It has deepened.
Private employers cut 32,000 jobs in November, according to ADP. Because the nation has been hemorrhaging jobs since President Trump took office, the administration has halted publishing the traditional monthly report. The ADP report revealed that small businesses suffered the heaviest losses. Establishments with fewer than 50 workers shed 120,000 positions, including 74,000 from companies with 20 to 49 workers. Larger firms added 90,000 jobs, widening the split between those rising and those falling.
Meanwhile, wealth continues to climb for the few who already possess most of it. Federal Reserve data shows the top 1 percent now holds $52 trillion. The top 10 percent added $5 trillion in the second quarter alone. The bottom half gained only 6 percent over the past year, a number so small it fades beside the towering fortunes above it.
“Less educated and poorer people tend to make worse mistakes,” John Campbell said to CBS News, while noting that the complexity of the system leaves many families lost before they even begin. Campbell, a Harvard University economist and coauthor of a book examining the country’s broken personal finance structure, pointed to a system built to confuse and punish those who lack time, training, or access.
“Creditors are just breathing down their necks,” Carol Fox told Bloomberg News, while noting that rising borrowing costs, shrinking consumer spending, and trade battles under the current administration have left owners desperate. Fox serves as a court-appointed Subchapter V trustee in Southern Florida and has watched the crisis unfold case by case.
During a cabinet meeting on Tuesday, Trump told those present that affordability “doesn’t mean anything to anybody.” He added that Democrats created a “con job” to mislead the public.
However, more than $30 million in taxpayer funds reportedly have supported his golf travel. Reports show Kristi Noem and FBI Director Kash Patel have also made extensive use of private jets through government and political networks. The administration approved a $40 billion bailout of Argentina. The president’s wealthy donors recently gathered for a dinner celebrating his planned $300 million White House ballroom.
During an appearance on CNBC, Mark Zandi, an economist, warned that the country could face serious economic threats. “We have learned that people make many mistakes,” Campbell added. “And particularly, sadly, less educated and poorer people tend to make worse mistakes.”
#NNPA BlackPress
The Numbers Behind the Myth of the Hundred Million Dollar Contract
BLACKPRESSUSA NEWSWIRE — Odell Beckham Jr. did not spark controversy on purpose. He sat on The Pivot Podcast and tried to explain the math behind a deal that looks limitless from the outside but shrinks fast once the system takes its cut.

By Stacy M. Brown
Black Press USA Senior National Correspondent
Odell Beckham Jr. did not spark controversy on purpose. He sat on The Pivot Podcast and tried to explain the math behind a deal that looks limitless from the outside but shrinks fast once the system takes its cut. He looked into the camera and tried to offer a truth most fans never hear. “You give somebody a five-year $100 million contract, right? What is it really? It is five years for sixty. You are getting taxed. Do the math. That is twelve million a year that you have to spend, use, save, invest, flaunt,” said Beckham. He added that buying a car, buying his mother a house, and covering the costs of life all chip away at what people assume lasts forever.
The reaction was instant. Many heard entitlement. Many heard a millionaire complaining. What they missed was a glimpse into a professional world built on big numbers up front and a quiet erasing of those numbers behind the scenes.
The tax data in Beckham’s world is not speculation. SmartAsset’s research shows that top NFL players often lose close to half their income to federal taxes, state taxes, and local taxes. The analysis explains that athletes in California face a state rate of 13.3 percent and that players are also taxed in every state where they play road games, a structure widely known as the jock tax. For many players, that means filing up to ten separate returns and facing a combined tax burden that reaches or exceeds 50 percent.
A look across the league paints the same picture. The research lists star players in New York, Philadelphia, Chicago, Detroit, and Cleveland, all giving up between 43 and 47 percent of their football income before they ever touch a dollar. Star quarterback Phillip Rivers, at one point, was projected to lose half of his playing income to taxes alone.
A second financial breakdown from MGO CPA shows that the problem does not only affect the highest earners. A $1 million salary falls to about $529,000 after federal taxes, state and city taxes, an agent fee, and a contract deduction. According to that analysis, professional athletes typically take home around half of their contract value, and that is before rent, meals, training, travel, and support obligations are counted.
The structure of professional sports contracts adds another layer. A study of major deals across MLB, the NBA, and the NFL notes that long-term agreements lose value over time because the dollar today has more power than the dollar paid in the future. Even the largest deals shrink once adjusted for time. The study explains that contract size alone does not guarantee financial success and that structure and timing play a crucial role in a player’s long-term outcomes.
Beckham has also faced headlines claiming he is “on the brink of bankruptcy despite earning over one hundred million” in his career. Those reports repeated his statement that “after taxes, it is only sixty million” and captured the disbelief from fans who could not understand how money at that level could ever tighten.
Other reactions lacked nuance. One article wrote that no one could relate to any struggle on eight million dollars a year. Another described his approach as “the definition of a new-money move” and argued that it signaled poor financial choices and inflated spending.
But the underlying truth reaches far beyond Beckham. Professional athletes enter sudden wealth without preparation. They carry the weight of family support. They navigate teams, agents, advisors, and expectations from every direction. Their earning window is brief. Their career can end in a moment. Their income is fragmented, taxed, and carved up before the public ever sees the real number.
The math is unflinching. Twenty million dollars becomes something closer to $8 million after federal taxes, state taxes, jock taxes, agent fees, training costs, and family responsibilities. Over five years, that is about $40 million of real, spendable income. It is transformative money, but not infinite. Not guaranteed. Not protected.
Beckham offered a question at the heart of this entire debate. “Can you make that last forever?”
#NNPA BlackPress
FBI Report Warns of Fear, Paralysis, And Political Turmoil Under Director Kash Patel
BLACKPRESSUSA NEWSWIRE — Six months into Kash Patel’s tenure as Director of the Federal Bureau of Investigation, a newly compiled internal report from a national alliance of retired and active-duty FBI agents and analysts delivers a stark warning about what the Bureau has become under his leadership.

Six months into Kash Patel’s tenure as Director of the Federal Bureau of Investigation, a newly compiled internal report from a national alliance of retired and active-duty FBI agents and analysts delivers a stark warning about what the Bureau has become under his leadership. The 115-page document, submitted to Congress this month, is built entirely on verified reporting from inside field offices across the country and paints a picture of an agency gripped by fear, divided by ideology, and drifting without direction.
The report’s authors write that they launched their inquiry after receiving troubling accounts from inside the Bureau only four months into Patel’s tenure. They describe their goal as a pulse check on whether the ninth FBI director was reforming the Bureau or destabilizing it. Their conclusion: the preliminary findings were discouraging.
Reports Describe Widespread Internal Distrust and Open Hostility Toward President Trump
Sources across the country told investigators that a large number of FBI employees openly express hostility toward President Donald Trump. One source reported seeing an “increasing number of FBI Special Agents who dislike the President,” adding that these employees were exhibiting what they called “TDS” and had lost “their ability to think critically about an issue and distinguish fact from fiction.” Another source described employees making off-color comments about the administration during office conversations.
The sentiment reportedly extends beyond domestic lines. Law enforcement and intelligence partners in allied countries have privately expressed fear that the Trump administration could damage long-term international cooperation according to a sub-source who reported those concerns directly to investigators.
Pardon Backlash and Fear of Retaliation
The President’s January 20 pardons of individuals convicted for their roles in the January 6 attack ignited what the report calls demoralization inside the Bureau. One FBI employee said they were “demoralized” that individuals “rightfully convicted” were pardoned and feared that some of those individuals or their supporters might target them or their family for carrying out their duties. Another source described widespread anger that lists of personnel who worked on January 6 investigations had been provided to the Justice Department for review, noting that agents “were just following orders” and now worry those lists could leak publicly.
Morale In Decline
Morale among FBI employees appears to be sinking fast. There were a few scattered positive notes, but the weight of the reporting describes morale as low, bad, or terrible. Agents with more than a decade of service told investigators they feel marginalized or ignored. Some are counting the days until they can retire. One even uses a countdown app on their phone.
Culture Of Fear
Layered over that unhappiness is something far more corrosive. A culture of fear. Sources say Patel, though personable, created mistrust from the start because of harsh remarks he made about the FBI before taking office. Agents took those comments personally. They now work in an atmosphere where employees keep their heads down and speak carefully. Managers wait for directions because they are afraid a wrong move could cost them their jobs. One source said agents dread coming to work because nobody knows who will be reassigned or fired next.
Leadership Concerns
The report also paints a picture of leaders unprepared for the jobs they hold. Multiple sources said Patel is in over his head and lacks the breadth of experience required to understand the Bureau’s complex programs. Some said Deputy Director Dan Bongino should never have been appointed because the role requires deep institutional knowledge of FBI operations. A sub-source recounted Bongino telling employees during a field office visit that “the truth is for chumps.” Employees who heard it were stunned and offended.
Social Media and Communication Breakdowns
Communication inside the Bureau has become another source of frustration. Sources said Patel and Bongino spend too much time posting on social media and not enough time communicating with employees in clear and official ways. Several told investigators they learn more about FBI operations from tweets than from internal channels.
ICE Assignments Raise Alarm
Nothing has sparked more frustration inside the FBI than the orders requiring agents to assist Immigration and Customs Enforcement. The reporting shows widespread resentment and fear over these assignments. Agents say they have little training in immigration law and were ordered into operations without proper planning. Some said they were put in tactically unsafe positions. They also warned that being pulled away from counterterrorism and counterintelligence investigations threatens national security. One sub-source asked, “If we’re not working CT and CI, then who is?”
DEI Program Removal
Even the future of diversity programs became a point of division. Some agents praised Patel’s removal of DEI initiatives. Others said the old system left them afraid to speak honestly because they worried about being labeled racist. The reporting shows a deep and unresolved conflict over whether DEI strengthened the organization or weakened it.
Notable Incidents
The document also details several incidents that have become part of FBI lore. Patel ordered all employees to remove pronouns and personal messages from their email signatures yet used the number nine in his own. Agents laughed at what they saw as hypocrisy. In another episode, FBI employees who discussed Patel’s request for an FBI-issued firearm were ordered to take polygraph examinations, which one respected source described as punitive. And in Utah, Patel refused to exit a plane without a medium-sized FBI raid jacket. A team scrambled to find one and finally secured a female agent’s jacket. Patel still refused to step out until patches were added. SWAT members removed patches from their own uniforms to satisfy the demand.
A Bureau at a Crossroad
The Alliance warns that the Bureau stands at a difficult crossroads. They write that the FBI faces some of the most daunting challenges in its history. But even in despair, a few voices say something different. One veteran source said “It is early, but most can see the mission is now the priority. Case work and threats are the focus again. Reform is headed in the right direction.”
-

 Bay Area3 weeks ago
Bay Area3 weeks agoPost Salon to Discuss Proposal to Bring Costco to Oakland Community meeting to be held at City Hall, Thursday, Dec. 18
-

 Activism3 weeks ago
Activism3 weeks agoMayor Lee, City Leaders Announce $334 Million Bond Sale for Affordable Housing, Roads, Park Renovations, Libraries and Senior Centers
-

 Activism3 weeks ago
Activism3 weeks agoOakland Post: Week of December 10 – 16, 2025
-

 Activism3 weeks ago
Activism3 weeks agoOakland School Board Grapples with Potential $100 Million Shortfall Next Year
-

 Arts and Culture3 weeks ago
Arts and Culture3 weeks agoFayeth Gardens Holds 3rd Annual Kwanzaa Celebration at Hayward City Hall on Dec. 28
-

 Activism3 weeks ago
Activism3 weeks ago2025 in Review: Seven Questions for Black Women’s Think Tank Founder Kellie Todd Griffin
-

 Advice3 weeks ago
Advice3 weeks agoCOMMENTARY: If You Don’t Want Your ‘Black Card’ Revoked, Watch What You Bring to Holiday Dinners
-

 Activism3 weeks ago
Activism3 weeks agoAnn Lowe: The Quiet Genius of American Couture


























































